Why Active Converters Are Necessary for Bridging Analog and Digital Signals
In today's interconnected world, the transition from analog to digital technology has brought significant advancements in audio-visual quality, speed, and efficiency. However, many legacy devices are in use by factories and some government organizations still rely on analog signals, while all modern devices primarily use digital signals. To bridge this gap, active converters are essential. This article explores why active converters are necessary and how they enable seamless communication between analog and digital devices.
Understanding the Analog-to-Digital Difference
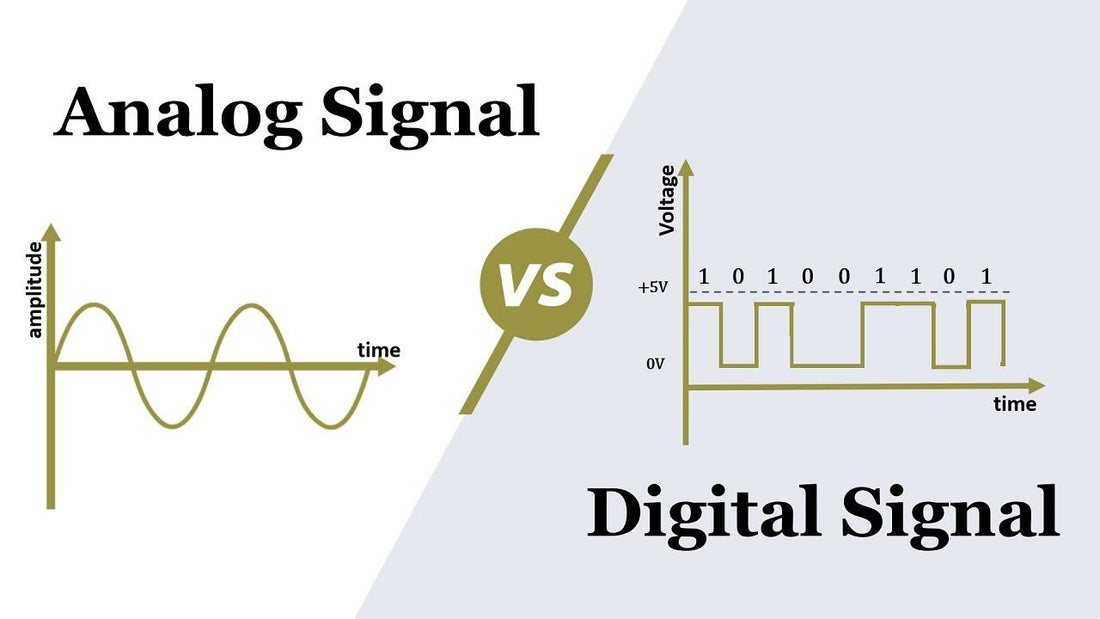
- Analog Signals: Represent data in continuous waveforms. Examples include VGA for video or RCA connectors for audio.
- Digital Signals: Represent data in discrete binary (0s and 1s). Examples include HDMI, DisplayPort, and thunderbolt for video and audio.
The fundamental difference lies in how information is transmitted: analog signals are continuous and susceptible to degradation, while digital signals are discrete and resistant to noise.
The Role of Active Converters
Active converters are specialized devices designed to translate analog signals into digital signals (and vice versa). Unlike passive converters, which only adapt physical connections, active converters include electronic components that actively process and convert the signal.
Why Passive Adapters Alone Won’t Work
Passive adapters may suffice when converting between different formats of the same signal type (e.g., DVI to HDMI), but they fail when the conversion involves analog-to-digital transformation or vice versa. Here’s why:
-
Signal Types Are Fundamentally Different
Analog signals are voltage-based waveforms, while digital signals consist of discrete binary data (0s and 1s). Without processing, an analog signal cannot be interpreted by a digital device. -
Digital Devices Require Specific Protocols
Digital devices expect data to follow specific encoding and timing protocols. A passive adapter cannot encode the analog signal to meet these requirements. -
No Native Communication Path
Analog signals cannot natively travel through digital connectors due to incompatible formats, making active conversion necessary.
Risks of Using Passive Converters
Passive converters lack powered circuitry and rely on direct wiring to connect analog and digital devices. While they are inexpensive, they are not suitable for most analog-to-digital conversions due to:
- Lack of Signal Processing: Passive converters cannot translate the fundamental differences between analog and digital signals.
- Reduced Quality: They often result in poor video or audio output due to signal degradation.
- Limited Compatibility: They only work when devices already support both analog and digital signal types internally, which is rare.
How Active Converters Work
Active converters contain components like analog-to-digital converters (ADCs) to perform the following tasks:
-
Signal Interpretation
The ADC reads the continuous analog waveform and samples it at regular intervals to measure the amplitude. -
Digital Encoding
The sampled data is encoded into a binary format that digital devices can understand. -
Output Optimization
Active converters optimize the digital signal to match the specifications of the output device, such as resolution, refresh rate, and aspect ratio.
Benefits of Using Active Converters
-
Seamless Compatibility
They allow legacy analog devices to work with modern digital equipment, extending their usability. -
High-Quality Signal Conversion
Active converters preserve the quality of the original signal, minimizing artifacts and distortion. -
Support for Advanced Features
Many active converters enable additional features like upscaling (enhancing resolution) and synchronization (maintaining audio-video alignment). -
Versatility
Active converters are available for various use cases, from connecting VGA to HDMI for video to converting RCA to optical for audio.
Examples of Applications
-
Home Theater Systems
Connecting an older DVD player (VGA or composite output) to a modern HDTV (HDMI input). -
Workplace Presentations
Using a legacy VGA projector with a laptop equipped with HDMI or DisplayPort output. -
Gaming Setups
Integrating retro gaming consoles with modern displays. -
Industrial/factory Environments
Bridging older analog equipment with digital monitoring systems.
Considerations When Choosing an Active Converter
- Signal Type: Ensure the converter supports the specific input and output signal formats.
- Resolution Support: Match the converter's resolution capabilities to your display requirements.
- Power Source: Some active converters require an external power supply to function.
- Latency: High-quality converters minimize latency, essential for gaming and video playback.
Conclusion
Active converters play a crucial role in bridging the gap between analog and digital devices. By translating incompatible signals, they enable seamless communication, extend the lifespan of legacy equipment, and provide flexibility in diverse applications. Whether for professional or personal use, investing in a reliable active converter ensures a high-quality connection and preserves your workflow or entertainment experience.